Your organization has resources in two different VPCs, each in different Google Cloud projects, and requires connectivity between the resources in the two VPCs. You have already determined that there is no IP address overlap; however, one VPC uses privately used public IP (PUPI) ranges. You would like to enable connectivity between these resources by using a lower cost and higher performance method. What should you do?
You are designing a Partner Interconnect hybrid cloud connectivity solution with geo-redundancy across two metropolitan areas. You want to follow Google-recommended practices to set up the following region/metro pairs:
(region 1/metro 1)
(region 2/metro 2)
What should you do?
Your company recently migrated to Google Cloud in a Single region. You configured separate Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks for two departments. Department A and Department B. Department A has requested access to resources that are part Of Department Bis VPC. You need to configure the traffic from private IP addresses to flow between the VPCs using multi-NIC virtual machines (VMS) to meet security requirements Your configuration also must
• Support both TCP and UDP protocols
• Provide fully automated failover
• Include health-checks
Require minimal manual Intervention In the client VMS
Which approach should you take?
Your company runs an enterprise platform on-premises using virtual machines (VMS). Your internet customers have created tens of thousands of DNS domains panting to your public IP addresses allocated to the Vtvls Typically, your customers hard-code your IP addresses In their DNS records You are now planning to migrate the platform to Compute Engine and you want to use Bring your Own IP you want to minimize disruption to the Platform What Should you d0?
Your company has a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with two Dedicated Interconnect connections in two different regions: us-west1 and us-east1. Each Dedicated Interconnect connection is attached to a Cloud Router in its respective region by a VLAN attachment. You need to configure a high availability failover path. By default, all ingress traffic from the on-premises environment should flow to the VPC using the us-west1 connection. If us-west1 is unavailable, you want traffic to be rerouted to us-east1. How should you configure the multi-exit discriminator (MED) values to enable this failover path?
Your software team is developing an on-premises web application that requires direct connectivity to Compute Engine Instances in GCP using the RFC 1918 address space. You want to choose a connectivity solution from your on-premises environment to GCP, given these specifications:
Your ISP is a Google Partner Interconnect provider.
Your on-premises VPN device’s internet uplink and downlink speeds are 10 Gbps.
A test VPN connection between your on-premises gateway and GCP is performing at a maximum speed of 500 Mbps due to packet losses.
Most of the data transfer will be from GCP to the on-premises environment.
The application can burst up to 1.5 Gbps during peak transfers over the Interconnect.
Cost and the complexity of the solution should be minimal.
How should you provision the connectivity solution?
Your organization wants to deploy HA VPN over Cloud Interconnect to ensure encryption-in-transit over the Cloud Interconnect connections. You have created a Cloud Router and two encrypted VLAN attachments that have a 5 Gbps capacity and a BGP configuration. The BGP sessions are operational. You need to complete the deployment of the HA VPN over Cloud Interconnect. What should you do?
Your organization has a hub and spoke architecture with VPC Network Peering, and hybrid connectivity is centralized at the hub. The Cloud Router in the hub VPC is advertising subnet routes, but the on-premises router does not appear to be receiving any subnet routes from the VPC spokes. You need to resolve this issue. What should you do?
You are configuring the firewall endpoints as part of the Cloud Next Generation Firewall (Cloud NGFW) intrusion prevention service in Google Cloud. You have configured a threat prevention security profile, and you now need to create an endpoint for traffic inspection. What should you do?
Your company’s on-premises network is connected to a VPC using a Cloud VPN tunnel. You have a static route of 0.0.0.0/0 with the VPN tunnel as its next hop defined in the VPC. All internet bound traffic currently passes through the on-premises network. You configured Cloud NAT to translate the primary IP addresses of Compute Engine instances in one region. Traffic from those instances will now reach the internet directly from their VPC and not from the on-premises network. Traffic from the virtual machines (VMs) is not translating addresses as expected. What should you do?
You recently deployed Compute Engine instances in regions us-west1 and us-east1 in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with default routing configurations. Your company security policy mandates that virtual machines (VMs) must not have public IP addresses attached to them. You need to allow your instances to fetch updates from the internet while preventing external access. What should you do?
Your organization has a Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with subnets in us-east1, us-west4, and europe-west4 that use the default VPC configuration. Employees in a branch office in Europe need to access the resources in the VPC using HA VPN. You configured the HA VPN associated with the Google Cloud VPC for your organization with a Cloud Router deployed in europe-west4. You need to ensure that the users in the branch office can quickly and easily access all resources in the VPC. What should you do?
Your company is running out of network capacity to run a critical application in the on-premises data center. You want to migrate the application to GCP. You also want to ensure that the Security team does not lose their ability to monitor traffic to and from Compute Engine instances.
Which two products should you incorporate into the solution? (Choose two.)
Question:
Your organization has a subset of applications in multiple regions that require internet access. You need to control internet access from applications to URLs, including hostnames and paths. The compute instances that run these applications have an associated secure tag. What should you do?
Your company is planning a migration to Google Kubernetes Engine. Your application team informed you that they require a minimum of 60 Pods per node and a maximum of 100 Pods per node Which Pod per node CIDR range should you use?
You are creating a new application and require access to Cloud SQL from VPC instances without public IP addresses.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose two.)
You are troubleshooting an application in your organization's Google Cloud network that is not functioning as expected. You suspect that packets are getting lost somewhere. The application sends packets intermittently at a low volume from a Compute Engine VM to a destination on your on-premises network through a pair of Cloud Interconnect VLAN attachments. You validated that the Cloud Next Generation Firewall (Cloud NGFW) rules do not have any deny statements blocking egress traffic, and you do not have any explicit allow rules. Following Google-recommended practices, you need to analyze the flow to see if packets are being sent correctly out of the VM to isolate the issue. What should you do?
You have created a firewall with rules that only allow traffic over HTTP, HTTPS, and SSH ports. While testing, you specifically try to reach the server over multiple ports and protocols; however, you do not see any denied connections in the firewall logs. You want to resolve the issue.
What should you do?
Your company's security team wants to limit the type of inbound traffic that can reach your web servers to protect against security threats. You need to configure the firewall rules on the web servers within your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to handle HTTP and HTTPS web traffic for TCP only. What should you do?
You want to deploy a VPN Gateway to connect your on-premises network to GCP. You are using a non BGP-capable on-premises VPN device. You want to minimize downtime and operational overhead when your network grows. The device supports only IKEv2, and you want to follow Google-recommended practices.
What should you do?
Your company is working with a partner to provide a solution for a customer. Both your company and the partner organization are using GCP. There are applications in the partner's network that need access to some resources in your company's VPC. There is no CIDR overlap between the VPCs.
Which two solutions can you implement to achieve the desired results without compromising the security? (Choose two.)
Question:
Your multi-region VPC has had a long-standing HA VPN configured in "region 1" connected to your corporate network. You are planning to add two 10 Gbps Dedicated Interconnect connections and VLAN attachments in "region 2" to connect to the same corporate network. You need to plan for connectivity between your VPC and corporate network to ensure that traffic uses the Dedicated Interconnect connections as the primary path and the HA VPN as the secondary path. What should you do?
You want to establish a dedicated connection to Google that can access Cloud SQL via a public IP address and that does not require a third-party service provider.
Which connection type should you choose?
You are designing a packet mirroring policy as pan of your network security architecture for your gaming workload. Your Infrastructure is located in the us-west2 region and deployed across several zones: us-west2-a. us-west2-b. and us-west2-c The Infrastructure Is running a web-based application on TCP ports 80 and 443 with other game servers that utilize the UDP protocol. You need to deploy packet mirroring policies and collector instances to monitor web application traffic while minimizing inter-zonal network egress costs.
Following Google-recommended practices, how should you deploy the packet mirroring policies and collector instances?
You have provisioned a Partner Interconnect connection to extend connectivity from your on-premises data center to Google Cloud. You need to configure a Cloud Router and create a VLAN attachment to connect to resources inside your VPC. You need to configure an Autonomous System number (ASN) to use with the associated Cloud Router and create the VLAN attachment.
What should you do?
You have configured Cloud CDN using HTTP(S) load balancing as the origin for cacheable content. Compression is configured on the web servers, but responses served by Cloud CDN are not compressed.
What is the most likely cause of the problem?
Your on-premises data center has 2 routers connected to your GCP through a VPN on each router. All applications are working correctly; however, all of the traffic is passing across a single VPN instead of being load-balanced across the 2 connections as desired.
During troubleshooting you find:
•Each on-premises router is configured with the same ASN.
•Each on-premises router is configured with the same routes and priorities.
•Both on-premises routers are configured with a VPN connected to a single Cloud Router.
•The VPN logs have no-proposal-chosen lines when the VPNs are connecting.
•BGP session is not established between one on-premises router and the Cloud Router.
What is the most likely cause of this problem?
You are configuring a new instance of Cloud Router in your Organization’s Google Cloud environment to allow connection across a new Dedicated Interconnect to your data center Sales, Marketing, and IT each have a service project attached to the Organization’s host project.
Where should you create the Cloud Router instance?
Your company has separate Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks in a single region for two departments: Sales and Finance. The Sales department's VPC network already has connectivity to on-premises locations using HA VPN, and you have confirmed that the subnet ranges do not overlap. You plan to peer both VPC networks to use the same HA tunnels for on-premises connectivity, while providing internet connectivity for the Google Cloud workloads through Cloud NAT. Internet access from the on-premises locations should not flow through Google Cloud. You need to propagate all routes between the Finance department and on-premises locations. What should you do?
Question:
Your organization's security team recently discovered that there is a high risk of malicious activities originating from some of your VMs connected to the internet. These malicious activities are currently undetected when TLS communication is used. You must ensure that encrypted traffic to the internet is inspected. What should you do?
Your company's security team tends to use managed services when possible. You need to build a dashboard to show the number of deny hits that occur against configured firewall rules without increasing operational overhead. What should you do?
You want to set up two Cloud Routers so that one has an active Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session, and the other one acts as a standby.
Which BGP attribute should you use on your on-premises router?
You have the following private Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster deployment:

You have a virtual machine (VM) deployed in the same VPC in the subnetwork kubernetes-management with internal IP address 192.168.40 2/24 and no external IP address assigned. You need to communicate with the cluster master using kubectl. What should you do?
You are responsible for designing a new connectivity solution for your organization's enterprise network to access and use Google Workspace. You have an existing Shared VPC with Compute Engine instances in us-west1. Currently, you access Google Workspace via your service provider's internet access. You want to set up a direct connection between your network and Google. What should you do?
Question:
Your organization wants to seamlessly migrate a global external web application from Compute Engine to GKE. You need to deploy a simple, cloud-first solution that exposes both applications and sends 10% of the requests to the new application. What should you do?
You are using a 10-Gbps direct peering connection to Google together with the gsutil tool to upload files to Cloud Storage buckets from on-premises servers. The on-premises servers are 100 milliseconds away from the Google peering point. You notice that your uploads are not using the full 10-Gbps bandwidth available to you. You want to optimize the bandwidth utilization of the connection.
What should you do on your on-premises servers?
Question:
Your organization wants to deploy HA VPN over Cloud Interconnect to ensure encryption in transit over the Cloud Interconnect connections. You have created a Cloud Router and two encrypted VLAN attachments that have a 5 Gbps capacity and a BGP configuration. The BGP sessions are operational. You need to complete the deployment of the HA VPN over Cloud Interconnect. What should you do?
You recently deployed two network virtual appliances in us-central1. Your network appliances provide connectivity to your on-premises network, 10.0.0.0/8. You need to configure the routing for your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Your design must meet the following requirements:
All access to your on-premises network must go through the network virtual appliances.
Allow on-premises access in the event of a single network virtual appliance failure.
Both network virtual appliances must be used simultaneously.
Which method should you use to accomplish this?
Question:
Recently, your networking team enabled Cloud CDN for one of the external-facing services that is exposed through an external Application Load Balancer. The application team has already defined which content should be cached within the responses. Upon testing the load balancer, you did not observe any change in performance after the Cloud CDN enablement. You need to resolve the issue. What should you do?
You are increasing your usage of Cloud VPN between on-premises and GCP, and you want to support more traffic than a single tunnel can handle. You want to increase the available bandwidth using Cloud VPN.
What should you do?
You are configuring your Google Cloud environment to connect to your on-premises network. Your configuration must be able to reach Cloud Storage APIs and your Google Kubernetes Engine nodes across your private Cloud Interconnect network. You have already configured a Cloud Router with your Interconnect VLAN attachments. You now need to set up the appropriate router advertisement configuration on the Cloud Router. What should you do?
You have two Google Cloud projects in a perimeter to prevent data exfiltration. You need to move a third project inside the perimeter; however, the move could negatively impact the existing environment. You need to validate the impact of the change. What should you do?
You are trying to update firewall rules in a shared VPC for which you have been assigned only Network Admin permissions. You cannot modify the firewall rules. Your organization requires using the least privilege necessary.
Which level of permissions should you request?
You converted an auto mode VPC network to custom mode. Since the conversion, some of your Cloud Deployment Manager templates are no longer working. You want to resolve the problem.
What should you do?
You need to create the network infrastructure to deploy a highly available web application in the us-east1 and us-west1 regions. The application runs on Compute Engine instances, and it does not require the use of a database. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do?
You are the network administrator responsible for hybrid connectivity at your organization. Your developer team wants to use Cloud SQL in the us-west1 region in your Shared VPC. You configured a Dedicated Interconnect connection and a Cloud Router in us-west1, and the connectivity between your Shared VPC and on-premises data center is working as expected. You just created the private services access connection required for Cloud SQL using the reserved IP address range and default settings. However, your developers cannot access the Cloud SQL instance from on-premises. You want to resolve the issue. What should you do?
Your company's web server administrator is migrating on-premises backend servers for an application to GCP. Libraries and configurations differ significantly across these backend servers. The migration to GCP will be lift-and-shift, and all requests to the servers will be served by a single network load balancer frontend. You want to use a GCP-native solution when possible.
How should you deploy this service in GCP?
Your company has defined a resource hierarchy that includes a parent folder with subfolders for each department. Each department defines their respective project and VPC in the assigned folder and has the appropriate permissions to create Google Cloud firewall rules. The VPCs should not allow traffic to flow between them. You need to block all traffic from any source, including other VPCs, and delegate only the intra-VPC firewall rules to the respective departments. What should you do?
Question:
Your company's current network architecture has three VPC Service Controls perimeters:
One perimeter (PERIMETER_PROD) to protect production storage buckets
One perimeter (PERIMETER_NONPROD) to protect non-production storage buckets
One perimeter (PERIMETER_VPC) that contains a single VPC (VPC_ONE)
In this single VPC (VPC_ONE), the IP_RANGE_PROD is dedicated to the subnets of the production workloads, and the IP_RANGE_NONPROD is dedicated to subnets of non-production workloads. Workloads cannot be created outside those two ranges. You need to ensure that production workloads can access only production storage buckets and non-production workloads can access only non-production storage buckets with minimal setup effort. What should you do?
Question:
Your organization has a hub and spoke architecture with VPC Network Peering, and hybrid connectivity is centralized at the hub. The Cloud Router in the hub VPC is advertising subnet routes, but the on-premises router does not appear to be receiving any subnet routes from the VPC spokes. You need to resolve this issue. What should you do?
You are adding steps to a working automation that uses a service account to authenticate. You need to drive the automation the ability to retrieve files from a Cloud Storage bucket. Your organization requires using the least privilege possible.
What should you do?
Your end users are located in close proximity to us-east1 and europe-west1. Their workloads need to communicate with each other. You want to minimize cost and increase network efficiency.
How should you design this topology?
You are designing an IP address scheme for new private Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) clusters. Due to IP address exhaustion of the RFC 1918 address space In your enterprise, you plan to use privately used public IP space for the new clusters. You want to follow Google-recommended practices. What should you do after designing your IP scheme?
You have created an HTTP(S) load balanced service. You need to verify that your backend instances are responding properly.
How should you configure the health check?
Your company has a single Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network deployed in Google Cloud with on-premises connectivity already in place. You are deploying a new application using Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), which must be accessible only from the same VPC network and on-premises locations. You must ensure that the GKE control plane is exposed to a predefined list of on-premises subnets through private connectivity only. What should you do?
You have the following Shared VPC design VPC Flow Logs is configured for Subnet-1 In the host VPC. You also want to monitor flow logs for Subnet-2. What should you do?
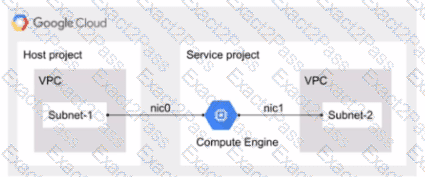
You deployed a hub-and-spoke architecture in your Google Cloud environment that uses VPC Network Peering to connect the spokes to the hub. For security reasons, you deployed a private Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster in one of the spoke projects with a private endpoint for the control plane. You configured authorized networks to be the subnet range where the GKE nodes are deployed. When you attempt to reach the GKE control plane from a different spoke project, you cannot access it. You need to allow access to the GKE control plane from the other spoke projects. What should you do?
You have several microservices running in a private subnet in an existing Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). You need to create additional serverless services that use Cloud Run and Cloud Functions to access the microservices. The network traffic volume between your serverless services and private microservices is low. However, each serverless service must be able to communicate with any of your microservices. You want to implement a solution that minimizes cost. What should you do?
You are responsible for configuring firewall policies for your company in Google Cloud. Your security team has a strict set of requirements that must be met to configure firewall rules.
Always allow Secure Shell (SSH) from your corporate IP address.
Restrict SSH access from all other IP addresses.
There are multiple projects and VPCs in your Google Cloud organization. You need to ensure that other VPC firewall rules cannot bypass the security team’s requirements. What should you do?
Your organization recently re-architected your cloud environment to use Network Connectivity Center. However, an error occurred when you tried to add a new VPC named vpc-dev as a spoke. The error indicated that there was an issue with an existing spoke and the IP space of a VPC named vpc-pre-prod. You must complete the migration quickly and efficiently. What should you do?