
Routers R1 through R4 are running an IGP in such a way that they have each other’s system IP addresses in their routing tables. A static route is configured on router R1 so that it can reach subnetwork 10.4.100.0/24. The network administrator decides to use an indirect static route, as shown in the diagram. However, pinging the server from router R1 fails. What may be the problem in this case?
Consider the exhibit.
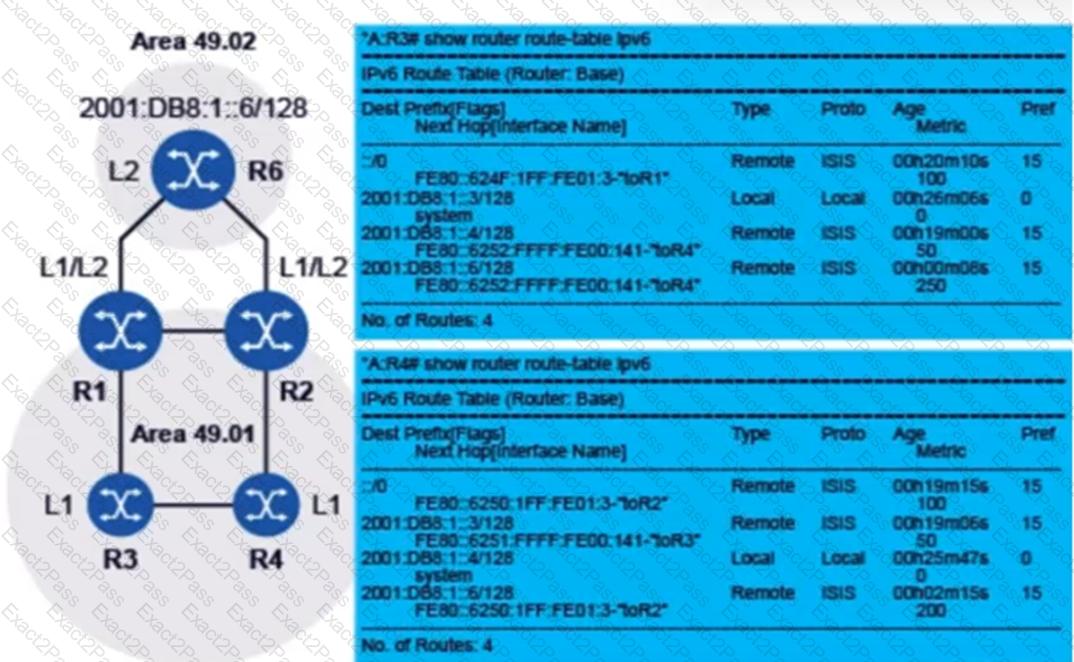
All routers are running IS-IS with IPv6 support enabled. Based on the topology shown, and the route tables of routers R3 and R4, which of the following statements is TRUE?
When a router performs the SPF calculation, which router is used as the root of the shortest path tree?

In the diagram, all routers are using IS-IS as their routing protocol. The number next to each link is its metric value.
What path will traffic follow from router R1 to router R7, and from router R7 to router R1?
Two IS-IS neighboring routers are trying to establish an adjacency, but the interface has been configured as broadcast on one of them and as point-to-point on the other. Why is the adjacency not established?

Examine the physical topology of the IS-IS network, the metrics of the links and the levels of the routers. All routers have their system interfaces included in IS-IS. Which of the following statements describes the route-table entry that router R4 will use to reach the system IP address of router R6?
There are several differences between IS-IS Hello packets used on broadcast interfaces and on point-to-point interfaces.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?