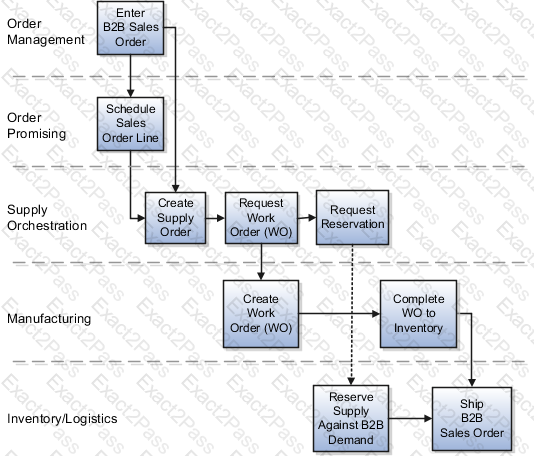
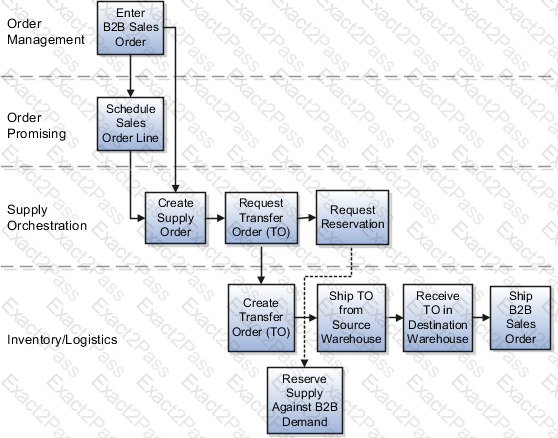
Set Up Back-to-Back Transfer Flow in Oracle Cloud
The Back-to-Back (B2B) Transfer Flow allows organizations to move inventory from one warehouse (source) to another warehouse (destination) when stock is unavailable in the fulfillment location. This setup ensures that Oracle Global Order Promising (GOP) can automatically determine the best supply source and execute the transfer process efficiently.
1. Prerequisites: Enable Back-to-Back for Items
Before setting up the transfer flow, ensure that the item is Back-to-Back enabled in Oracle Product Information Management (PIM):
Navigate to Oracle Product Information Management (PIM).
Search for the item you want to enable for back-to-back fulfillment.
In the item definition, enable the "Back-to-Back Enabled" attribute.
Save and publish the item updates.
✅ This ensures that the item can participate in the B2B fulfillment process.
2. Configure Global Order Promising (GOP) for Back-to-Back Transfer Flow
In Oracle Global Order Promising (GOP), configure the system to determine the best transfer source when fulfilling back-to-back orders.
Step 1: Create a Global Sourcing Rule (Type: Transfer From)
Navigate to Oracle Global Order Promising (GOP).
Create a Global Sourcing Rule with the following details:
✅ This rule ensures that items are sourced from Warehouse 1 whenever stock is available.
Step 2: Create a Local Sourcing Rule (Type: Transfer From)
Create a Local Sourcing Rule for Warehouse 1 as follows:
✅ This rule ensures that if Warehouse 1 does not have stock, the system transfers items from Warehouse 2.
Step 3: Set Up an ATP Rule for Availability Check
Create an ATP Rule (Available-to-Promise Rule) with the following parameters:
Promising Mode: "Supply Chain Availability Search".
Enable attributes for supply chain availability search based on business needs.
Configure ATP search to consider on-hand stock, in-transit inventory, components, and resources if needed.
✅ This ensures that GOP can evaluate stock levels across multiple locations.
Step 4: Assign ATP Rule to Organizations
Assign the ATP Rule to the appropriate organizations.
Ensure that the rule applies to Warehouse 1 and Warehouse 2 based on their roles in the sourcing process.
✅ This enables availability checking when processing sales orders.
Step 5: Assign Sourcing Rules to Organizations
Assign the Global Sourcing Rule to the enterprise-wide sourcing assignment.
Assign the Local Sourcing Rule to Warehouse 1, specifying Warehouse 2 as the sourcing location.
Ensure that the assignment level for the global sourcing rule does not include a specific organization (it should apply at a broader level).
✅ This ensures that Oracle GOP prioritizes sourcing stock from Warehouse 1 first and transfers from Warehouse 2 if needed.
Step 6: Refresh and Restart Order Promising Server
Once the sourcing rules and ATP configurations are in place:
Refresh Oracle Global Order Promising (GOP) Rules.
Restart the Order Promising Server to apply sourcing and ATP rule changes.
✅ This step ensures that all updates take effect and are used in future order promising decisions.
3. Expected Behavior After Setup
If Warehouse 1 has stock → GOP reserves inventory and processes the sales order immediately.
If Warehouse 1 does not have stock → GOP triggers a transfer order to move stock from Warehouse 2 to Warehouse 1.
Once the transfer order is fulfilled and received, the sales order is shipped to the customer.
✅ This ensures automated order fulfillment with minimal manual intervention.
4. Benefits of Back-to-Back Transfer Flow in Oracle Cloud
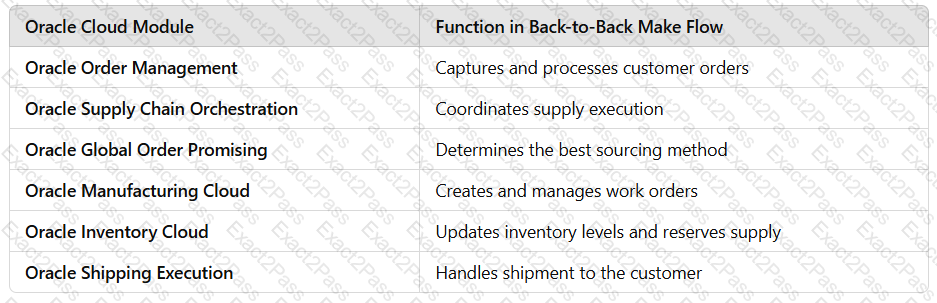
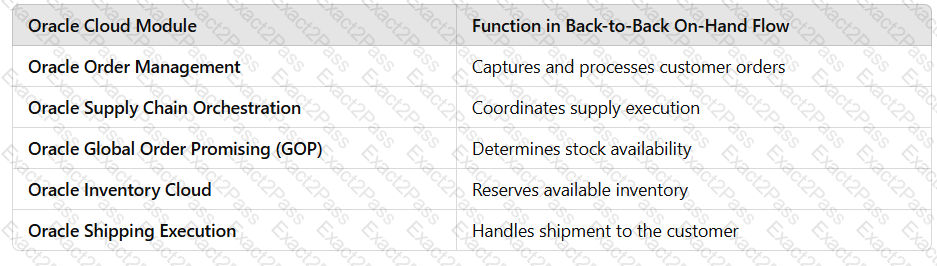
✔ Optimized Inventory Utilization – Uses stock efficiently across multiple warehouses.✔ Automated Stock Transfers – Eliminates manual intervention by automatically moving stock when needed.✔ Reduced Procurement Costs – Moves existing inventory instead of purchasing new stock.✔ Faster Order Fulfillment – Reduces lead times by sourcing from internal stock before procurement.✔ Seamless Oracle Cloud Integration – Works across Oracle Order Management, Inventory, GOP, and Supply Chain Orchestration.





 A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.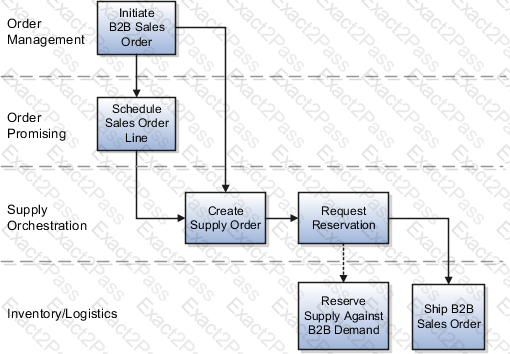
 A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.
A screenshot of a computer
AI-generated content may be incorrect.