Last Update 7 hours ago Total Questions : 326
The Oracle Database 12c SQL content is now fully updated, with all current exam questions added 7 hours ago. Deciding to include 1z0-071 practice exam questions in your study plan goes far beyond basic test preparation.
You'll find that our 1z0-071 exam questions frequently feature detailed scenarios and practical problem-solving exercises that directly mirror industry challenges. Engaging with these 1z0-071 sample sets allows you to effectively manage your time and pace yourself, giving you the ability to finish any Oracle Database 12c SQL practice test comfortably within the allotted time.
Which two statements are true about Oracle synonyms?
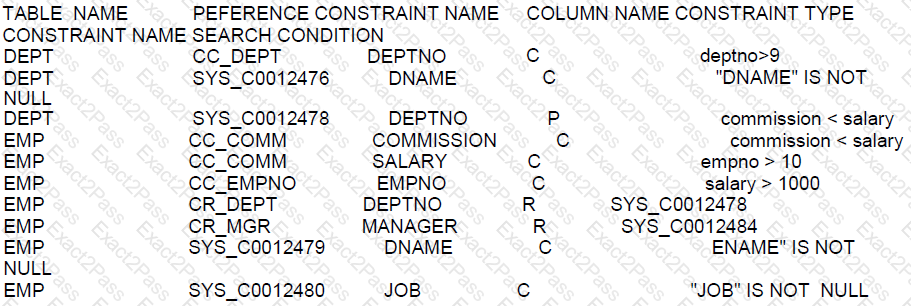
Which three statements are true?
Examine this query:
SELECT SUBSTR (SYSDATE,1,5) ‘Result’ FROM DUAL
Which statement is true?
Which two statements are true about an Oracle database?
Examine the description of the PRODUCT_INFORMATION table:

Which two statements are true? (Choose two.)
Which two statements are true about CURRENT_TIMEITAMP?

